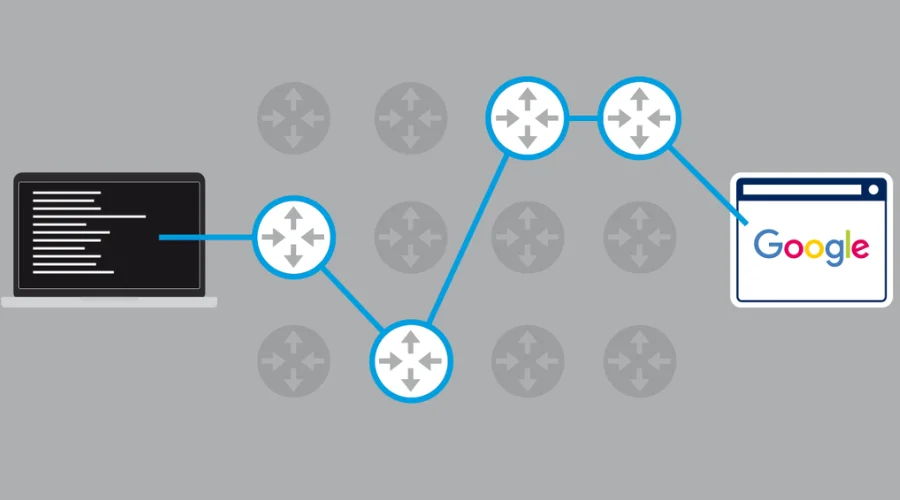
Tracert, an abbreviation for “trace route,” is a network diagnostic tool used to determine the path and measure the network latency between your computer and a target host or IP address. By employing a series of ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) or UDP (User Datagram Protocol) packets, tracert provides invaluable insights into the network infrastructure, identifying potential bottlenecks and troubleshooting connectivity issues.
Tracert operates by sending a series of packets to the destination IP address, incrementally increasing the “time to live” (TTL) value for each subsequent packet. The TTL value determines the maximum number of hops (routers) a packet can traverse before being discarded. As each packet encounters a router, the router decrements the TTL value and, if it reaches zero, the router discards the packet and sends an ICMP “Time Exceeded” message back to the source.
Tracert Functionality:
1. Identifying Network Path:
Tracert reveals the path taken by packets from your computer to the target IP address. It lists each hop along the way, including the IP addresses of intermediate routers and their response times. Bluehost leverages this feature to identify potential network congestion points, ensuring efficient routing for its clients’ websites and applications.
2. Measuring Latency:
Tracert measures the time taken for packets to travel between each hop, providing insights into latency issues. By analyzing the response times, Bluehost can detect latency spikes, allowing for prompt troubleshooting and performance optimizations.
3. Troubleshooting Network Connectivity:
Tracert is an invaluable tool for diagnosing connectivity issues. If a tracert command fails to reach the target IP address, it provides valuable information about the point of failure. Bluehost utilizes this feature to isolate and resolve connectivity problems, minimizing downtime for its customers.
4. Assessing Network Performance:
By analyzing the tracert output, Bluehost can assess the overall performance of the network infrastructure. It helps them identify bottlenecks, optimize routing paths, and ensure smooth data transmission for their clients.
Performing a Traceroute with Bluehost: A step-by-step guide
Traceroute is a valuable network diagnostic tool that allows you to track the path of your internet connection from your computer to a specific destination server. It helps identify network latency and pinpoint potential issues along the way.
1. Open a Command Prompt or Terminal:
To begin, open the Command Prompt on Windows or Terminal on macOS or Linux. You can typically find these utilities by searching for “Command Prompt” or “Terminal” in your computer’s search bar.
2. Launch the Traceroute Command:
Once you have the Command Prompt or Terminal open, type the following command to initiate the Traceroute process:
tracert www.example.com
In this command, replace “www.example.com” with the actual domain name or IP address of the server you want to trace the route to. Tracert is a Windows-specific command, while the equivalent command on macOS and Linux is “traceroute.”
3. Analyze the Traceroute Results:
After executing the Traceroute command, you will see a list of network hops, along with their IP addresses and response times. Each hop represents a router or gateway that your connection passes through on its way to the destination server. The response times indicate the latency experienced at each hop.
Pay attention to any unusually high response times or asterisks (*) indicating packet loss. These can be indications of network congestion or connectivity issues. Traceroute allows you to identify the specific hop where the problem arises.
4. Save the Traceroute Output:
It’s a good practice to save the Traceroute results for future reference or when seeking support from Bluehost or other network administrators. To save the output, use the following command:
tracert www.example.com > traceroute.txt
This command saves the output to a file named “traceroute.txt” in the current directory. Feel free to choose a different name or location for the file if desired.
5. Share the Traceroute Results:
If you encounter network issues and need assistance from Bluehost support, it’s helpful to share the Traceroute results with them. You can either copy and paste the contents of the “traceroute.txt” file into an email or support ticket, or attach the file itself.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Tracert is an essential network diagnostic tool that enables organizations like Bluehost to ensure optimal network performance for their clients. By providing insights into network paths, measuring latency, troubleshooting connectivity issues, and assessing network performance, tracert plays a crucial role in maintaining a reliable and efficient network infrastructure. For more information visit Bluehost and the official website of Findwyse.